The explosive growth of data has created an unprecedented demand for skilled data scientists. These professionals are the linchpins of data-driven decision-making, transforming raw data into actionable insights that propel innovation across diverse sectors. While a formal degree can provide a structured foundation, it’s not a prerequisite for a successful career in this field. This comprehensive guide from Melsoft Academy will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to embark on a rewarding data science journey, even without a traditional degree. We’ll explore the fundamentals of data science, detail the essential skills, and provide a step-by-step roadmap to help you build a compelling career.
Key Takeaways:
- A data science degree isn’t mandatory; a strong skillset and proven problem-solving abilities are paramount.
- Master core programming languages (Python, R, SQL), statistical analysis, and machine learning algorithms.
- Construct a compelling portfolio of data science projects using publicly available datasets and personal initiatives.
- Actively network within the data science community to gain insights, mentorship, and job opportunities.
- Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for staying ahead in this rapidly evolving field.
Understanding Data Science
Data science is a multidisciplinary field that integrates mathematical expertise, computer programming skills, and business acumen to extract meaningful knowledge from data. It’s a holistic process encompassing data collection, cleaning (handling missing values, outliers, inconsistencies), exploration (visualization, summary statistics), analysis (statistical modeling, machine learning), and interpretation (communicating findings to stakeholders). The goal is to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within datasets to inform strategic decisions and drive innovation.
The field’s origins trace back to the early 2000s, with the formal coining of the term “data science” reflecting the growing need to integrate statistical methods with computational power to handle increasingly large and complex datasets. Today, data science leverages a wide array of techniques, including:
- Descriptive Analytics: Summarizing and visualizing data to understand past performance.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Identifying the root causes of past events.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting future outcomes based on historical data and statistical models.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Recommending actions to optimize future outcomes.
Data scientists utilize various tools and programming languages, including Python, R, SQL, and specialized data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI, to manage, analyze, and interpret data effectively.
Why Choose a Data Science Career?
The appeal of a data science career extends far beyond the financial rewards. Here are compelling reasons to consider this path:
- High Demand and Growth: The industry is experiencing explosive growth, creating a consistently high demand for skilled professionals. This translates to numerous job opportunities and a strong competitive advantage in the job market. The World Economic Forum has consistently highlighted data science roles as among the fastest-growing and most in-demand professions globally.
- Lucrative Compensation: The expertise required to transform complex data into actionable strategies commands high salaries, placing data science among the most lucrative career paths. Compensation varies based on experience, location, and specialization, but the earning potential is substantial.
- Diverse Career Paths: The field offers a wide range of specializations, allowing you to tailor your career path to your interests and skills. These include:
- Data Scientist: Focuses on building predictive models and extracting insights from data.
- Data Analyst: Concentrates on analyzing data to provide actionable insights and reports.
- Data Engineer: Designs and builds data infrastructure and pipelines.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Develops and deploys machine learning models.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Focuses on using data to improve business decision-making.
- Impactful Work: Data scientists contribute to projects that have a tangible impact on various aspects of society, from healthcare and finance to environmental science and social justice. The work is often intellectually stimulating and socially relevant.
- Continuous Learning and Innovation: The field is dynamic and constantly evolving, requiring continuous learning and adaptation. This keeps the work engaging and challenging, preventing professional stagnation.
Essential Skills for Data Scientists
To succeed in data science, you need a robust skillset encompassing technical proficiency, analytical abilities, and effective communication. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas:
- Mathematics: A solid foundation in calculus, linear algebra, and probability and statistics is essential. Calculus is crucial for understanding optimization algorithms used in machine learning. Linear algebra is fundamental for handling high-dimensional data. Probability and statistics are the cornerstones of data analysis and model building.
- Programming: Proficiency in Python or R is essential. Python’s extensive libraries (Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn) make it particularly well-suited for data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning. R excels in statistical computing and data visualization. SQL is also crucial for interacting with databases.
- Statistical Analysis: Mastering statistical concepts like hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and experimental design is crucial for drawing valid conclusions from data. Understanding different statistical distributions and their applications is also vital.
- Machine Learning: A deep understanding of machine learning algorithms (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning), model evaluation metrics, and model selection techniques is necessary for building predictive models.
- Data Wrangling and Preprocessing: This involves cleaning, transforming, and preparing data for analysis. Skills in handling missing data, outliers, and inconsistent data formats are crucial.
- Data Visualization: The ability to effectively communicate insights through visualizations (charts, graphs, dashboards) is critical for conveying complex information to both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Communication and Collaboration: Data scientists need to effectively communicate their findings and recommendations to stakeholders, often requiring strong written and verbal communication skills, as well as the ability to collaborate effectively within teams.
- Domain Knowledge: Understanding the specific industry or domain you’re working in is crucial for interpreting data accurately and providing relevant insights.
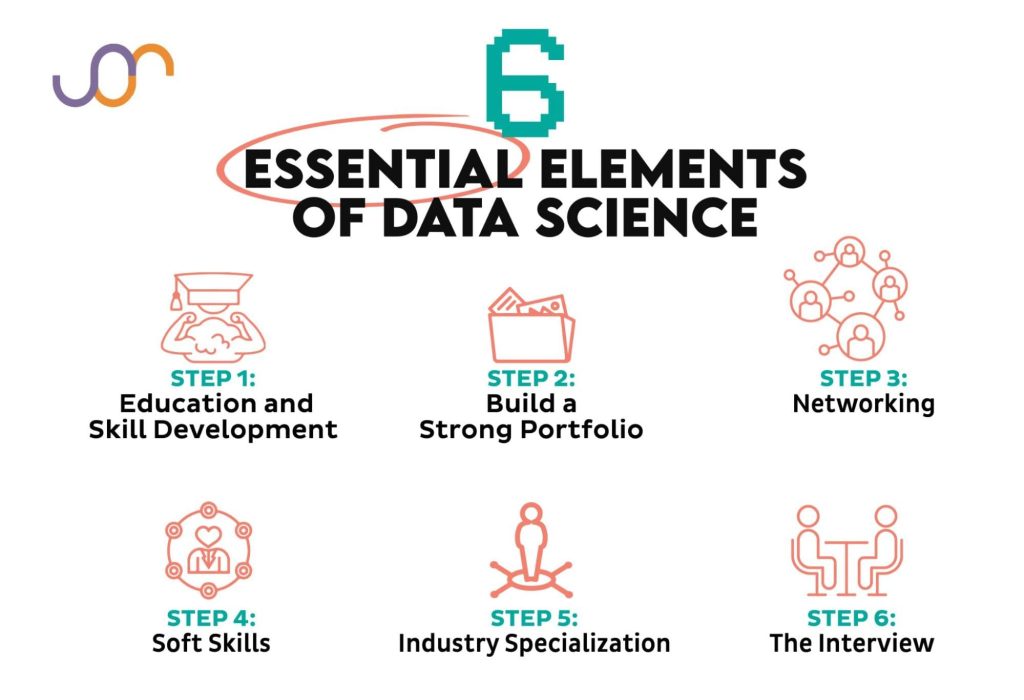
Building Your Data Science Skills Without a Degree
Mastering the Data Universe: Key Steps to a Thriving Data Science Career – KDnuggets
The absence of a formal degree doesn’t preclude a successful data science career. Here’s a structured approach to building your skills:
1. Structured Online Learning:
Several platforms offer high-quality data science courses and tutorials. While we won’t name specific platforms here, a simple online search for “free data science courses” or “data science tutorials” will yield numerous options. Look for courses that cover the essential skills outlined above. Focus on hands-on practice and completing projects to solidify your understanding.
2. Targeted Skill Development:
Instead of broad, general courses, focus your learning on specific skills relevant to your desired data science role. For example, if you’re interested in machine learning, concentrate on courses and tutorials that cover specific algorithms, model evaluation, and hyperparameter tuning.
3. Immersive Learning Projects:
The best way to learn data science is by doing. Undertake several projects using publicly available datasets from sources like Kaggle, UCI Machine Learning Repository, and government open data portals. Start with simpler projects and gradually increase the complexity. Document your projects thoroughly, including your methodology, code, and results. This will form the foundation of your portfolio.
4. Personal Projects:
Identify problems you’re passionate about and try to solve them using data science. This could involve analyzing sports statistics, predicting stock prices, or creating a recommendation system. These projects demonstrate your initiative and problem-solving abilities.
5. Contribute to Open Source:
Contributing to open-source projects on platforms like GitHub allows you to collaborate with experienced data scientists, learn from their code, and build your reputation within the community.
6. Networking and Community Engagement:
Attend data science meetups, conferences, and online forums to connect with other professionals. This provides invaluable opportunities for mentorship, collaboration, and learning from experienced practitioners.
Building Your Portfolio and Job Search Strategy

3 ways to build data science portfolio to stand out
Your portfolio is your most valuable asset. It showcases your skills and abilities to potential employers. Include a diverse range of projects that demonstrate your proficiency in different areas of data science. Clearly describe your methodology, code, and results for each project. Use platforms like GitHub to host your code and make it easily accessible.
When applying for jobs, emphasize your skills and experience, even without a formal degree. Highlight your accomplishments and the value you can bring to the organization. A strong portfolio and demonstrable skills will outweigh the absence of a degree. Tailor your resume and cover letter to each specific job application, emphasizing the skills and experience most relevant to the role.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The field of data science is constantly evolving. New techniques, tools, and algorithms are continuously emerging. To stay competitive, you need to commit to continuous learning. Regularly explore new technologies, attend workshops and conferences, and stay updated on the latest research and trends.
Conclusion
A fulfilling and successful career in data science is achievable without a traditional degree. By focusing on acquiring the essential skills, building a strong portfolio, and actively engaging with the data science community, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic and rewarding field. Embrace continuous learning, network effectively, and showcase your abilities – the path to becoming a data scientist is open to you. Begin your journey today!



Itѕ like you read my mind! Ⲩou аppear to ҝnow ѕo much about this, likе you wrote the book in it or something.
I think that you could do with some piсs to drive the message home a little bit,
but other than that, this is fantastic blog. An excellent read.
I’ll certainly be back.
Thіs info is priceless. Where can I find oսt more?
When someone ᴡrites an post he/she retains the image օf a user in his/her mind that how a user can be aware of it.
So that’s why this paragraph is perfect. Thanks!