Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses operate, offering on-demand access to computing resources over the internet. Three giants dominate this landscape: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). While all three provide similar core services, significant differences exist in their strengths, weaknesses, and target audiences. This article delves into these key distinctions to help you understand which platform best suits your needs.
What is AWS?

Amazon Web Services (AWS), launched in 2006, is the oldest and currently the largest cloud provider. Its early adoption and continuous innovation have solidified its position as a market leader. AWS offers a vast and comprehensive suite of services, encompassing compute (EC2), storage (S3), databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, and much more. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, minimizing costs.
Key Features of AWS:
- Extensive Service Catalog: AWS boasts the most extensive range of services among the three platforms, catering to a wide array of use cases.
- Mature Ecosystem: Years of development have resulted in a robust and mature ecosystem, with a large community of developers, partners, and readily available documentation.
- Global Infrastructure: AWS operates a massive global infrastructure spanning numerous regions and availability zones, ensuring high availability and low latency.
- Strong Developer Tools: AWS provides a rich set of developer tools and services, simplifying the process of building, deploying, and managing applications.
AWS Regions and Availability: AWS is divided into numerous geographic regions, each containing multiple availability zones (AZs). This distributed infrastructure enhances resilience and fault tolerance.
What is Azure?
Microsoft Azure, launched in 2010, is a powerful cloud platform offering a comprehensive set of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions. Its strong integration with Microsoft’s existing software and services makes it particularly attractive to organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. Azure provides robust capabilities in areas like virtual machines, databases, analytics, AI, and IoT.
Key Features of Azure:
- Strong Microsoft Integration: Azure seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products and services, such as Windows Server, Active Directory, and SQL Server. This simplifies migration and management for organizations heavily reliant on Microsoft technologies.
- Hybrid Cloud Capabilities: Azure offers robust hybrid cloud capabilities, allowing organizations to easily connect their on-premises infrastructure with the cloud.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Azure prioritizes security, offering a range of features and services to protect data and applications.
- Competitive Pricing: Azure often offers competitive pricing, particularly for organizations using a significant number of Microsoft products.
Azure Regions and Availability: Azure maintains a global network of regions and availability zones, comparable to AWS in terms of geographic reach and redundancy.
What is Google Cloud?
Google Cloud Platform (GCP), launched in 2008, leverages Google’s extensive experience in data management and analytics. GCP excels in areas like big data processing, machine learning, and container orchestration (Kubernetes). Its infrastructure is built on the same technology that powers Google’s own services, offering scalability and performance advantages.
Key Features of GCP:
- Big Data and Analytics: GCP offers leading-edge big data and analytics capabilities, powered by technologies like BigQuery and Dataflow.
- Machine Learning Expertise: GCP provides a strong suite of machine learning tools and services, including TensorFlow, a widely used open-source machine learning framework.
- Kubernetes Expertise: GCP is a pioneer in container orchestration, with its Kubernetes engine (GKE) being a popular choice for deploying and managing containerized applications.
- Strong Developer Tools: GCP provides a range of developer tools and services, catering to modern development practices.
GCP Regions and Availability: GCP also boasts a global network of regions and zones, providing high availability and low latency.
Key Tools: A Comparative Look
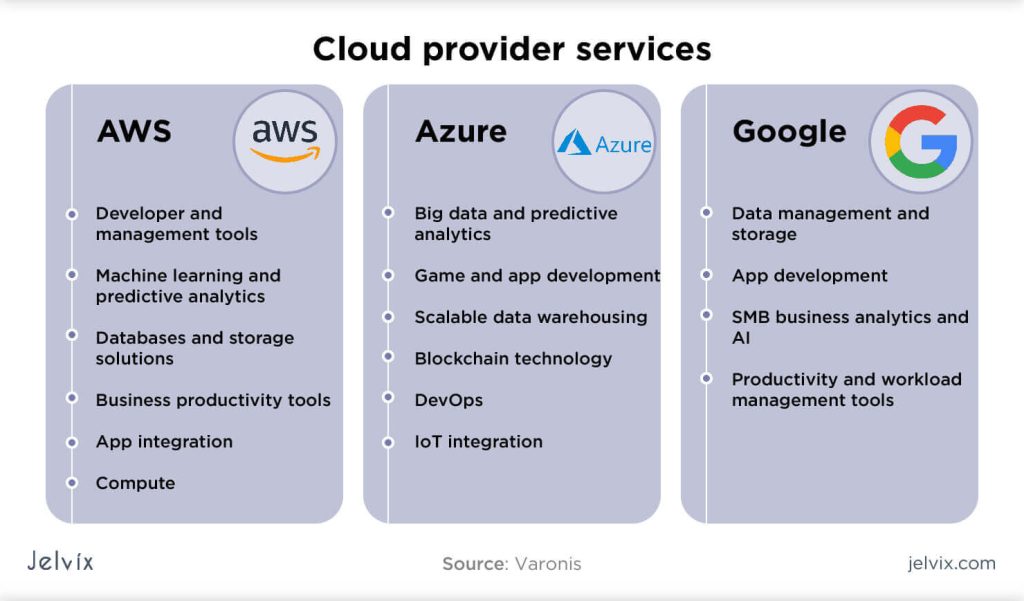
All three platforms offer a wide range of tools and services. However, their strengths lie in different areas:
AWS Key Tools:
- AI/ML: AWS offers services like SageMaker (for training and deploying machine learning models), Rekognition (for image and video analysis), and Comprehend (for natural language processing).
- Serverless Computing: AWS Lambda allows developers to run code without managing servers.
- IoT: AWS IoT Core provides a platform for connecting and managing IoT devices.
Azure Key Tools:
- Cognitive Services: Azure offers a suite of cognitive services, including vision, speech, and language APIs.
- IoT Hub: Azure IoT Hub provides a secure and scalable platform for connecting and managing IoT devices.
- Serverless Computing: Azure Functions offers a serverless computing platform similar to AWS Lambda.
Google Cloud Key Tools:
- BigQuery: A highly scalable and cost-effective data warehouse.
- TensorFlow: A widely used open-source machine learning framework.
- Kubernetes Engine (GKE): A managed Kubernetes service.
- Serverless Computing: Google Cloud Functions offers a serverless computing platform.
Benefits and Considerations
When considering the right cloud platform, it’s essential to evaluate your specific needs and priorities. Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out with the largest market share and the broadest range of services, supported by a mature ecosystem and extensive community backing, offering high reliability and security. However, its complexity can be daunting for beginners, and the pricing structure may be intricate and potentially expensive if not managed properly.
In contrast, Microsoft Azure offers strong integration with Microsoft technologies and excellent hybrid cloud capabilities, making it a competitive option for organizations heavily invested in Microsoft products. Its pricing can be favorable for these users, but it has a smaller service catalog compared to AWS, which may limit its appeal for others.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) excels in big data and analytics, showcasing robust capabilities in machine learning and Kubernetes, often proving cost-effective for specific workloads. Nevertheless, GCP has a smaller market share and community compared to AWS and Azure, and it may lack maturity or feature richness in certain areas. Therefore, choosing the right platform involves weighing these benefits and considerations carefully.
Which Cloud Platform Should You Choose?
The best cloud platform for you depends on several factors:
- Existing infrastructure: If you’re heavily invested in Microsoft technologies, Azure might be the most logical choice.
- Specific needs: If you require advanced big data or machine learning capabilities, GCP might be a better fit.
- Budget: All three offer competitive pricing, but careful cost analysis is crucial.
- Developer expertise: The familiarity of your development team with a specific platform’s tools and services is a key consideration.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. A thorough evaluation of your business requirements, technical expertise, and budget is essential to making the right decision. Consider experimenting with free tiers offered by each provider to gain hands-on experience before committing to a long-term solution.
Career Prospects for Cloud Developers
The demand for skilled cloud developers is high and continues to grow. Proficiency in any of these platforms—AWS, Azure, or GCP—is a valuable asset in the job market. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest technologies within your chosen platform are essential for career advancement. The cloud computing field is dynamic, and professionals who adapt to evolving technologies and maintain strong skills will be highly sought after.
Download Our Prospectus: Download Prospectus
About Melsoft Academy: Learn More
Apply Now: Apply Here
Apply to the Manati Alternate Student Funding: Apply for Funding