Key Takeaways
- The Bank of Uganda confirmed a cyber attack, but disputes the initially reported $17 million loss.
- Investigations by the Criminal Investigations Department and Auditor General are underway, with potential insider involvement a key focus.
- The incident highlights the growing cyber threats facing financial institutions in Africa and the need for robust cybersecurity strategies.
- The controversy surrounding the actual amount stolen raises concerns about transparency and accountability.
What Happened at the Bank of Uganda?

In late November 2024, the normally placid waters of Uganda’s financial landscape were roiled by news of a significant cyber attack targeting the nation’s central bank. Initial reports, citing local media outlets like the New Vision newspaper, painted a dramatic picture: a group of hackers, self-identified as “Waste,” had allegedly penetrated the Bank of Uganda’s IT infrastructure, making off with a staggering $17 million (equivalent to 62 billion Ugandan shillings). This news sent shockwaves through the country and raised immediate concerns about the security of Uganda’s financial system.
However, the Bank of Uganda, while acknowledging the breach, swiftly moved to counter the narrative, asserting that the actual amount stolen was significantly less than the widely circulated figure. This discrepancy immediately ignited a firestorm of controversy and fueled speculation about the true extent of the damage, the effectiveness of the bank’s security protocols, and the potential for a cover-up.
The $17 Million Question: How Much Was Really Stolen?
The conflicting reports surrounding the amount of money stolen have created a cloud of confusion and raised serious questions about transparency and the accuracy of initial assessments. The government’s downplaying of the losses has been met with considerable skepticism from various quarters, including opposition politicians and independent media outlets. This skepticism is further fueled by the ongoing investigation, which is yet to release its conclusive findings.
Adding to the complexity, different media sources have reported varying figures, ranging from the initial $17 million to significantly lower sums, making it challenging to ascertain the true financial impact of the attack. The final audit report, expected in the coming weeks, is now eagerly anticipated to provide clarity and shed light on the true scale of the losses, which is crucial for both public understanding and the development of effective remedial measures.
Was it an Inside Job?
One of the most troubling aspects of this cyber attack is the allegation of insider involvement. Reports suggest that individuals within the Bank of Uganda, potentially motivated by financial gain or other factors, may have colluded with the external hackers, either actively participating in the breach or passively enabling it through negligence or compromised credentials. This possibility raises profound concerns about the integrity of internal security protocols, the effectiveness of background checks for employees, and the potential for vulnerabilities stemming from compromised personnel.
The ongoing investigation must meticulously examine these claims, scrutinizing communication logs, access records, and financial transactions to determine the extent, if any, of internal complicity. Understanding the potential role of insiders is critical not only for holding those responsible accountable but also for implementing effective security measures to prevent similar breaches in the future. This includes strengthening internal controls, enhancing employee training on cybersecurity best practices, and implementing robust monitoring systems to detect suspicious activity.
How Did the Hackers Breach the Bank of Uganda’s Security?
While the precise details of how the hackers managed to infiltrate the Bank of Uganda’s systems are still shrouded in secrecy due to the ongoing investigation, cybersecurity experts have speculated on several potential vulnerabilities that could have been exploited. These include phishing attacks, where employees are tricked into revealing sensitive information like passwords through deceptive emails or messages; malware infections, where malicious software is installed on bank computers, allowing hackers to gain control of systems; or exploiting weaknesses in the bank’s network infrastructure, such as unpatched software or poorly configured firewalls.
The investigation will likely focus on identifying the specific attack vector used, analyzing network traffic logs, examining compromised systems, and conducting forensic analysis to understand the hackers’ methods. This information will be crucial in determining how to prevent similar breaches in the future and strengthen the bank’s overall cybersecurity posture.
The Impact of the Cyber Attack on Uganda’s Financial Security
This cyber attack has far-reaching implications for Uganda’s financial security and overall economic stability. It exposes vulnerabilities within the country’s central banking system, raising concerns about the safety of financial assets, the integrity of financial transactions, and the potential for further attacks. The incident could erode public trust not only in the Bank of Uganda but also in the broader financial sector, potentially impacting the stability of the Ugandan shilling and investor confidence.
The government’s response to this crisis, including the transparency and thoroughness of the investigation, the implementation of robust remedial measures, and the communication of these actions to the public, will be crucial in restoring confidence and mitigating the long-term consequences of the attack. Furthermore, this incident should serve as a catalyst for a comprehensive review of cybersecurity practices across the entire financial sector in Uganda.
Cybersecurity in Africa
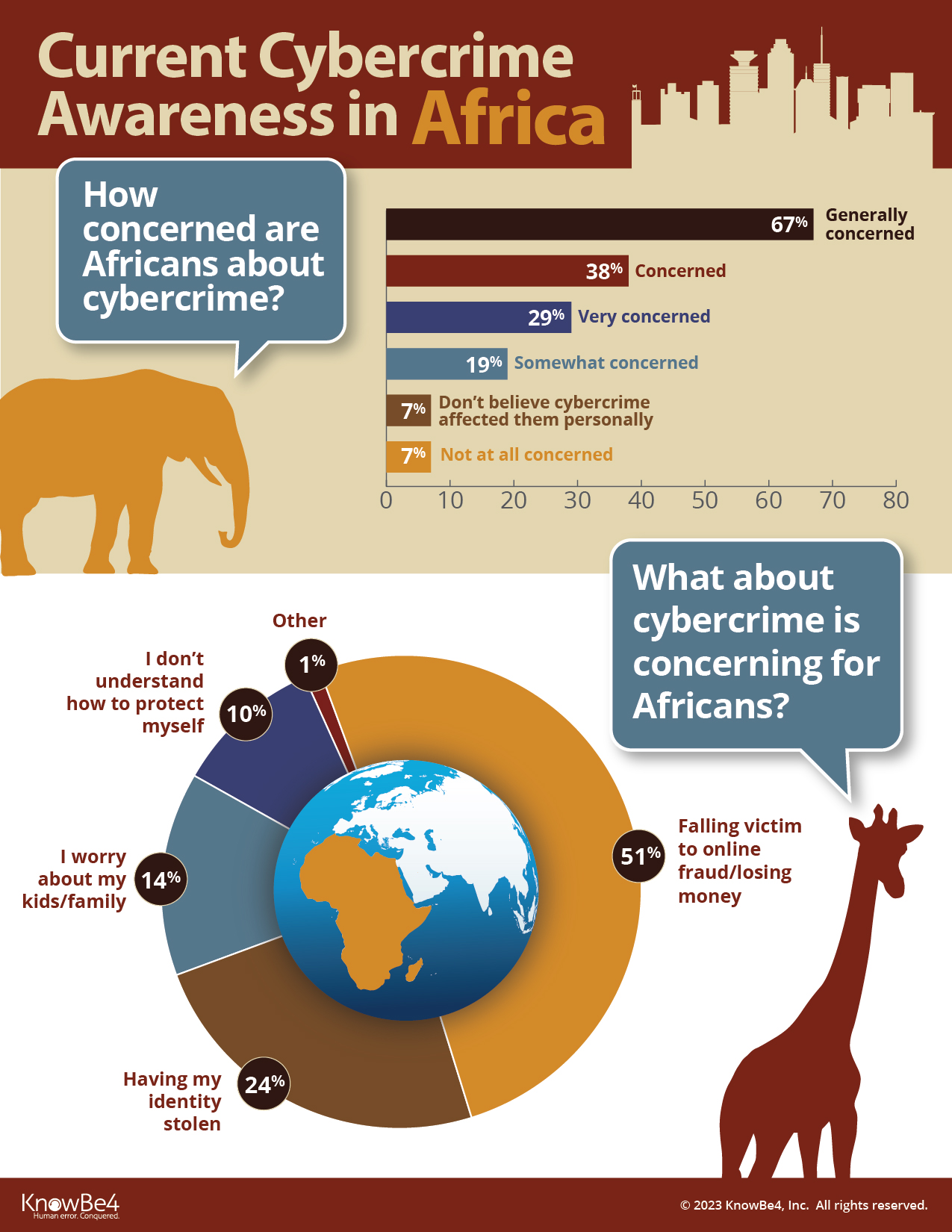
The Bank of Uganda cyber attack is not an isolated incident. It highlights the increasing frequency and growing sophistication of cyber threats targeting financial institutions and other critical infrastructure across the African continent. As African economies become increasingly digitalized, with greater reliance on online banking, mobile money transfers, and other digital financial services, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands significantly. Many banks and financial service providers in the region still lack robust cybersecurity infrastructure, adequate security expertise, and sufficient awareness among staff, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals seeking financial gain.
This incident underscores the urgent need for increased investment in cybersecurity measures, capacity building initiatives, and regional cooperation to share information and best practices to protect against future attacks and strengthen the overall cybersecurity posture of the African financial landscape. This includes investing in advanced security technologies, developing national cybersecurity strategies, and promoting cybersecurity awareness among businesses and the general public.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Defenses and Building Resilience
The Bank of Uganda cyber attack offers valuable lessons for financial institutions and other organizations worldwide. It emphasizes the critical importance of implementing strong cybersecurity protocols, including multi-factor authentication to verify user identities, regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities, robust incident response plans to manage and mitigate breaches, and continuous monitoring of systems for suspicious activity. Furthermore, organizations must prioritize employee cybersecurity training to raise awareness about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and other methods used by hackers to gain access to sensitive information.
Investing in advanced threat detection and prevention technologies, such as intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, is also essential to proactively identify and mitigate potential cyber threats before they can cause significant damage. Finally, fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and responsibility across the entire organization, from the boardroom to the front lines, is crucial for building a strong and resilient cybersecurity posture.
What’s Next for the Bank of Uganda and Cybersecurity in Uganda?
In the wake of this significant cyber attack, the Bank of Uganda faces the challenging task of rebuilding public trust, strengthening its cybersecurity defenses, and implementing the necessary reforms to prevent future incidents. The findings of the ongoing investigation will be crucial in informing these efforts and shaping the bank’s cybersecurity strategy moving forward. This incident should serve as a wake-up call not only for the Bank of Uganda but also for the Ugandan government and other financial institutions in the country to prioritize cybersecurity and invest in the necessary resources, both human and technological, to protect against the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.
A comprehensive national cybersecurity strategy, encompassing regulatory frameworks, public-private partnerships, and capacity building initiatives, is needed to address the growing cyber threats facing Uganda and ensure the security and stability of its financial system. This includes promoting cybersecurity awareness among businesses and the general public, fostering collaboration between government agencies and the private sector, and investing in research and development to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much money was stolen in the Bank of Uganda cyber attack?
Initial reports indicated a loss of $17 million, but the Bank of Uganda disputes this figure, claiming a significantly lower amount. The exact amount remains under investigation and is a point of contention.
2. Who were the hackers responsible for the attack?
A group identifying themselves as “Waste,” reportedly based in Southeast Asia, has been linked to the attack. However, their precise identity and location are still being investigated.
3. Was there any insider involvement in the cyber attack?
Allegations of insider involvement are a key focus of the ongoing investigation. Authorities are examining the possibility that individuals within the bank may have colluded with the hackers.
4. How did the hackers gain access to the Bank of Uganda’s systems?
The specific method used by the hackers to breach the bank’s security is still under investigation. Potential attack vectors include phishing, malware, exploiting software vulnerabilities, or a combination of these methods.
5. What is the impact of the cyber attack on Uganda’s economy?
The attack has the potential to erode public trust in the financial system, impacting the stability of the Ugandan shilling, investor confidence, and potentially slowing economic growth. The long-term impact will depend on the government’s response and the effectiveness of remedial measures.
6. What measures are being taken to prevent future cyber attacks?
The Bank of Uganda is expected to strengthen its cybersecurity protocols, implement stricter security measures, invest in advanced threat detection technologies, and enhance employee training on cybersecurity best practices. A broader national cybersecurity strategy is also anticipated.
7. What can other financial institutions learn from this incident?
This incident serves as a valuable lesson for financial institutions globally, highlighting the importance of robust cybersecurity defenses, proactive threat detection, regular security assessments, and a culture of cybersecurity awareness throughout the organization.
Conclusion
The Bank of Uganda cyber attack serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present and evolving threat of cybercrime in today’s interconnected world. This incident underscores the need for constant vigilance, proactive security measures, continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices, and a commitment to building a resilient cybersecurity posture. The investigation’s outcome will be crucial in shaping future cybersecurity strategies, not only for the Bank of Uganda but also for financial institutions across Africa and globally.
In an increasingly digital world, cybersecurity professionals are in high demand. If you’re passionate about technology and want to make a real difference in protecting organizations from cyber threats, a career in cybersecurity could be the perfect fit for you. Melsoft Academy offers comprehensive bootcamps designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge you need to thrive in this dynamic and rewarding field. Our expert instructors provide hands-on training in the latest cybersecurity technologies and techniques, preparing you for a successful career in this critical industry.
Take the first step towards your dream job!
Explore our cybersecurity bootcamps and gain the skills to safeguard critical financial systems.


